Managing NoSQL Database on IBM Cloudant
Cloudant is a fully managed and distributed Database as a Service (DBaaS) platform from IBM to create and manage NoSQL (Not only SQL) JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) documents. It is highly scalable, available and secured. Horizontal scaling, geo load balancing, auto sharding and rebalancing of data, and integrated IO monitoring and prioritization have made Cloudnat massively scalable(Source). Data in Cloudant is also highly available because it triplicates data in three different servers, and performs auto sharding and rebalancing to avoid the effect of server failure and maintenance. Data gets various security measures provided by the hosts such as certification, virus scanning and so on. Cloudant also ensures access security through authentication, encryption etc.
Differences Between NoSQL Cloudant and Relational DBMS SQL
Unlike SQL DBMS, Cloudant does not require designing of tables, relationships and datatypes. While an entity is usually distributed over several tables in SQL, it is a single document in Cloudant. Therefore, retrieving an entity does not require join operation as we may need in SQL. Furthermore, each entity can have a different structure in Cloudant that SQL does not allow. There is also no need for remodelling in Cloudant if entity structure changes. Besides, keeping an empty attribute with a Null value is unnecessary in Cloudant. Specifying Cloudant query is completely different from SQL. Furthermore, Cloudant is specially designed to support faceted search using Lucene Query Parser Syntax.
Cloudant Architecture
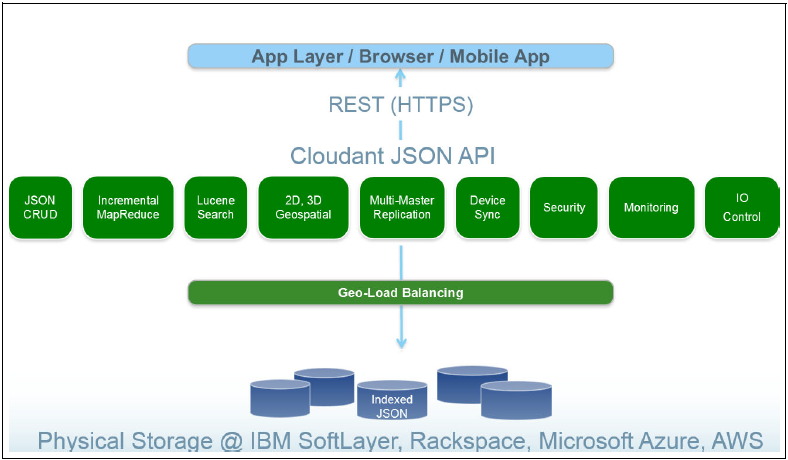
Figure 1 shows the Cloudant architecture (Source). Cloudant is physically hosted on IBM Softlayer, Amazon Web Services, Rackspace and Microsoft Azure. From the application layer users communicate with the services offered by Cloudant through its RESTful API. These services are built on top of a Geo-Load balancer that makes use of the available infrastructure.
Accessing Cloudant Database
At first, a user needs to create a Cloudant service in IBM Bluemix or in the Cloudant website. Then Cloudant database can be accessed in two ways- using the RESTful API or the web interface.
Figure.1 - Cloudant Archnitecture
Cloudant provides different client libraries (Source) for developers to write their programs to access and manage databases using the API. Command line tools are supported too to use the API.
Cloudant web interface also provides facilities for all kinds of database activities including query and search. It provides editors for writing the data to be stored, query instructions and indexes.
Data Model, Query and Search
Cloudant is a document-oriented database. Each entity is considered as a single document and stored in a semi-structured form using JSON, and assigned an identifier and revision number.
On the stored documents, Cloudant supports query and faceted search. It allows JSON query syntax for query and Lucene Query Parser Syntax for search.
Database Creation in Cloudant
The following steps were followed to create a database in Cloudant and to upload data from Data.txt file.
- At first, a Cloudant service was created in the Bluemix cloud named Cloudant NoSQL DB-nm.
- Python programs were developed
- To use the Cloudant API to establish connection with the created service.
- To create the database it uses the methods provided in the Cloudant package.
- It converts the supplied data to JSON format and uploads them to the database.
- Finally, it terminates the session by disconnecting from the server.
Table 1 lists the methods used to create and store data. It does not show built-in methods. Table 1: List of special methods used for creating database and uploading data (Source)
| Package | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Cloudant | Cloudant(cloudant_user, auth_token, **kwargs) connect() create_database(dbname, **kwargs) create_document(data, throw_on_exists=False) disconnect() |
Encapsulate a Cloudant client and manages session. Starts authentication and session. Creates database in the server. Stores documents in the database. Disconnects and ends a session. |
| csv | DictReader | Reads data from the user’s machine |
| time | sleep() | Delays the next instruction. |
Using API might be a bit challenging at starting, but it is very convenient to use to create database and to upload data once learned.
Retrieving data from the Database
After creating a search index on the member_id field of the uploaded data using the web interface, the following steps were followed to perform query and search on the created database.
- Another python program was used to establishe a session with the database using the API.
- It executes the specified select and search queries on the database to retrieve data.
- Finally, it terminates the session with the Cloudant database.
Table 2 lists the special methods used to perform query and search. In addition to these the methods from Table 1 was also used to establish communication with the database.
Table 2: List of methods used for performing query and search on the databa
| Package | Method | Purpose |
|:————-|:——————|:——|
|cloudant.database|cloudant.database.CloudantDatabase(client, database_name, fetch_limit=100)
get_query_result(selector, fields=None, raw_result=False, **kwargs)
get_search_result(ddoc_id, index_name, **query_params)|Instantiates cloudant database object.
Retrieves documents based on the specified query.
Retrieves documents based on the query specified in the search.|
Sample Query and Search
Q1: Find all reviews from member A1004AX2J2HXGL.
selector = {'member_id': {'$eq': 'A1004AX2J2HXGL'}}
docs_collection = my_cl_db_handler.get_query_result(selector)
Q2: Find the number of reviews by each member.
resp = my_cl_db_handler.get_search_result(ddoc_id='py_ddoc', index_name='py_index', query='*:*', counts=["member_id"])
Q3: Find the product ids of all products with at least one review rating less than 3.
selector = {'rating': {'$lt': 3}}
fields = ['product id']
docs_collection = my_cl_db_handler.get_query_result(selector, fields)